Table of contents
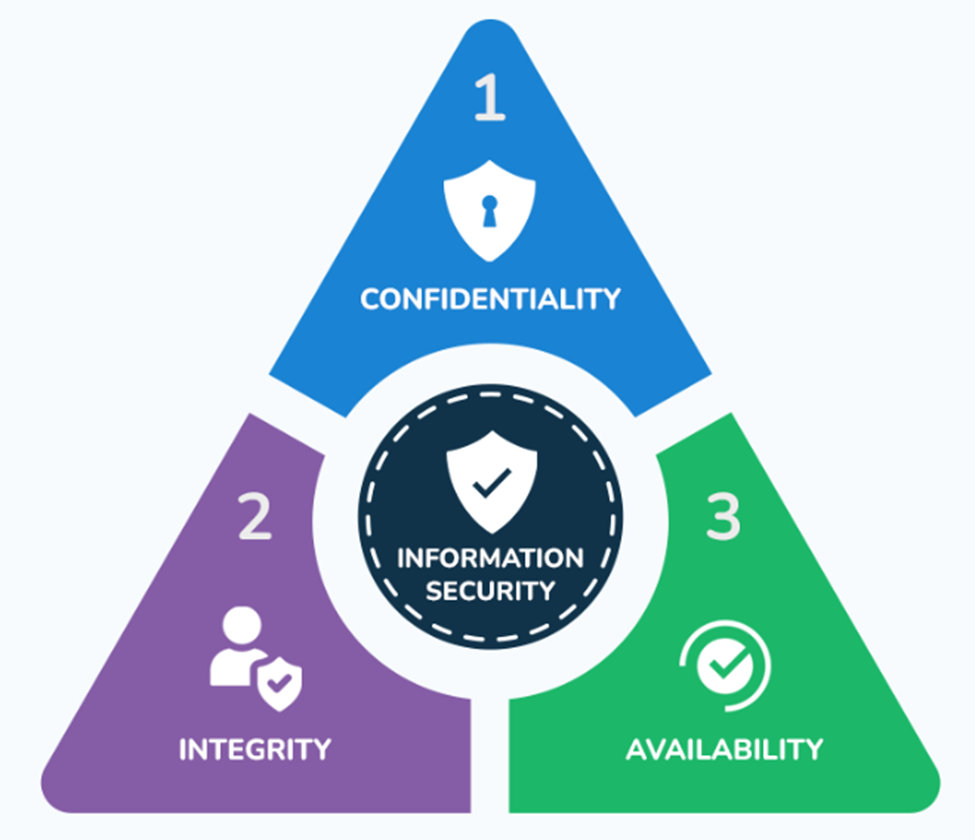
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
- The importance of the CIA Triad
- Security strategies based on the CIA Triad
Information security is a top priority for keeping digital data safe.
Computer systems are constantly threatened by attacks that can compromise sensitive data.
The CIA Triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability) represents the three fundamental pillars to ensure information security.
Understanding and implementing the CIA Triad in cyber security is important for:
- Protecting data from breaches
- Ensuring operational continuity
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is the first component of the CIA Triad and focuses on protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Confidentiality ensures that only authorized users can access confidential information.
This protection can be achieved through:
- The use of encryption techniques
- Multi-factor authentication
- Strict access controls
Example:
In banks, customer information must be accessible only to authorized personnel to prevent fraud and identity theft.
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) also play a crucial role in monitoring and preventing unauthorized access.
Integrity
Data integrity is the second component of the CIA Triad.
Ensuring data integrity means making sure that data is accurate and not altered without authorization.
Protecting data integrity is fundamental to maintaining trust in digital archives and information systems.
Techniques used to verify that data has not been tampered with include:
- Hashing
- Checksums
- Version controls
Example:
In financial transactions, data integrity is critical to prevent fraudulent transactions or errors in customer accounts.
Availability
Data availability is the third component of the CIA Triad.
This principle ensures that data and systems are accessible when needed.
Availability is important for the daily operations of any company as data must be readily available to authorized users.
Interruptions such as power outages, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and hardware failures can compromise availability.
Implementing information security strategies is essential to ensure operational continuity.
These include:
- Regular data backups
- The use of redundant servers
- Proactive security measures
The importance of the CIA Triad
The importance of the CIA Triad in cybersecurity cannot be understated.
Each component of the triad works in synergy to provide comprehensive information protection.
The lack of one of these elements can lead to serious consequences such as data breaches, loss of customer trust, and significant financial damage.
Adopting a CIA Triad-based approach allows companies to develop robust and resilient security measures, thereby protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data.
Security strategies based on the CIA Triad
To effectively implement the CIA Triad, organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach to information security.
Here are some security strategies that can be adopted:
Confidentiality strategy
- Encryption
Encryption is a fundamental technique to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Using advanced encryption algorithms, data is transformed into an unreadable format that can only be decrypted with the correct key.
There are two main types of encryption:
- Symmetric
Where the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt data
- Asymmetric
Which uses a pair of public and private keys.
End-to-end encryption is useful for protecting data during transmission between two points.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple authentication methods.
These can include something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (like a security token), and something the user is (like a fingerprint or facial recognition).
MFA reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if one of the verification methods is compromised.
- Access controls
Access controls determine who can view and interact with data within a system.
There are various access control models, including:
- Discretionary access control (DAC)
- Mandatory access control (MAC)
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
The RBAC model is particularly effective as it assigns permissions based on user roles, ensuring that each person has access only to the information necessary to perform their job.
Integrity strategy
- Hashing
Hashing creates a unique, fixed representation of the original data through a hash function.
Even a minimal alteration in the original data produces a completely different hash, making it easy to detect unauthorized changes.
Common hashing algorithms include MD5, SHA-1, and SHA-256, each offering different levels of security.
- Checksums
Checksums are values calculated from the original data that help detect errors during transmission or storage.
When data is received or read, a new checksum is calculated and compared with the original.
If the two values do not match, it means the data has been altered. Checksums are often used in communication networks to ensure the integrity of transmitted data.
- Version control
Version control is essential for tracking and managing file changes over time.
Systems like Git allow maintaining a detailed history of changes, making it possible to restore previous versions in case of error or unauthorized alteration.
This is particularly useful in software development projects and document management.
- Digital signatures
Digital signatures use asymmetric encryption to ensure that a document or message has not been altered.
A digital signature is generated using the signer’s private key and can be verified with the corresponding public key.
This process not only guarantees data integrity but also confirms its authenticity and origin.
Availability strategy
- Regular backups
Performing regular data backups is one of the most effective measures to ensure availability.
Backups allow restoring data in case of hardware failures, cyber attacks, or other incidents.
It is important to have a backup strategy that includes offsite copies and periodic restoration tests to ensure backups are functional and up-to-date.
- Redundancy and failover
Implementing system redundancy and failover mechanisms ensures that if one component fails, another can take its place without interruption.
This can include the use of duplicate servers, backup power supplies, and alternative networks.
Example:
Data centers often use redundant architectures to ensure operational continuity even during failures or maintenance.
- Protection against DoS attacks
Denial of service (DoS) attacks aim to make a system’s services unavailable by overloading it with traffic.
Protection measures against DoS attacks include:
- The use of firewalls
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- Load balancing to manage excess traffic
Content distribution networks (CDNs) can also help mitigate the impact of these attacks by distributing traffic across multiple servers.
- Continuous monitoring
Continuous monitoring of systems is essential to quickly detect and respond to any issues that could compromise availability.
Using real-time monitoring tools to:
- Track system performance
- Detect anomalies
- Alert administrators in case of problems
This approach helps prevent unexpected downtime and maintain data and service accessibility.
In conclusion, the CIA Triad is the foundation of information security.
Understanding and implementing the principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability is essential for protecting sensitive data and ensuring operational continuity.
In an increasingly digital world, organizations must adopt proactive and resilient security measures to address evolving threats.
FAQ
- What is the CIA Triad in cyber security?
The CIA Triad in cyber security consists of three fundamental principles: confidentiality, integrity, and availability, which ensure the protection of sensitive data. - Why is data confidentiality important?
Data confidentiality is important to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and prevent fraud and identity theft. - How can data integrity be ensured?
Data integrity can be ensured through techniques like hashing, checksums, and version control, which ensure that data has not been altered without authorization. - What is meant by data availability?
Data availability refers to the ability to access data and systems when needed, ensuring operational continuity. - What are the consequences of a data breach?
A data breach can lead to loss of customer trust, significant financial damage, and possible legal penalties. - How can organizations improve information security?
Organizations can improve information security by adopting encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular backups, continuous monitoring, and staff training. - What is a denial of service (DoS) attack?
A denial of service (DoS) attack is a cyber attack aimed at making a system’s services unavailable by overloading them with traffic. - What is the role of intrusion detection systems (IDS)?
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor suspicious activities in computer systems and help detect and respond quickly to security incidents. - Why are data backups important?
Data backups are important to prevent information loss in case of hardware failures, cyber attacks, or other emergencies. - What security measures can prevent power outages?
Measures such as the use of backup generators, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and redundant servers can help prevent the impact of power outages on data availability.

